English
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Telephone: +86 13120555503
Email: frank@cypump.com
Nov . 07, 2024 22:04 Back to list
Manual Guidance for Submersible Sewage Pumping System Operation and Maintenance Procedures
Submersible Sewage Pumping System Manual Operation and Maintenance
Submersible sewage pumping systems are essential components in modern waste management, offering efficient solutions for transporting wastewater from lower to higher elevations. Often submerged in sewage pits or basins, these pumps are designed to operate underwater, thus minimizing the risk of flooding and ensuring the smooth flow of sewage to treatment facilities. This article explores the manual operation and maintenance of submersible sewage pumping systems, highlighting key considerations to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Understanding Submersible Sewage Pumps
Submersible pumps are motor-driven units encased in a watertight housing, which enables them to work efficiently while submerged. They are typically equipped with a cutting mechanism to handle solid waste materials, making them ideal for sewage applications. Their design allows for direct pumping of sewage without requiring any priming, unlike traditional centrifugal pumps.
Manual Operation of Submersible Sewage Pumps
While many submersible sewage pumps are automated, understanding the manual operation is crucial for situations where automatic systems fail. Here are the steps for manual operation
1. Safety Precautions Before operating the pump, it's essential to ensure safety protocols are followed. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and make sure to isolate electrical supply before inspection or manual handling.
2. Check Pre-Operation Parameters Inspect the pump for any visible damages, such as cracks or leaks. Ensure that the power supply is connected and functioning properly. Verify that float switches (if applicable) are operating correctly.
3. Start-Up Procedures To manually start the pump, ensure all valves in the discharge line are open, and the pump is positioned in the correct orientation within the sewage basin. Power on the pump using the manual switch. Observe the pump's operation for any signs of abnormal sounds or vibrations.
4. Monitoring Once the pump is operational, monitor its performance continuously. Keep an eye on discharge pressure and flow rates. In the event of low flow or pump failure, there may be a need for prompt intervention.
'submersible sewage pumping system manual operation and ...'
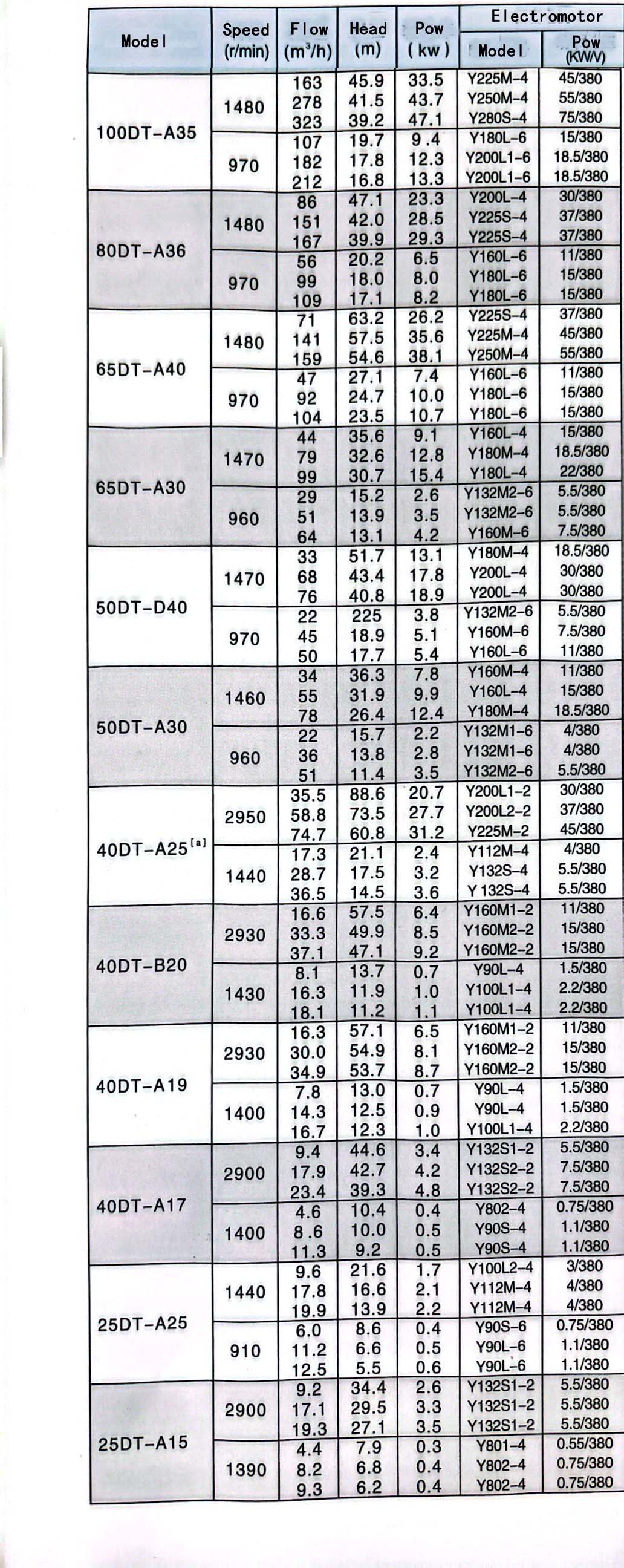
Maintenance of Submersible Sewage Pumps
Regular maintenance is vital to extend the service life of submersible sewage pumps. The following maintenance practices are recommended
1. Routine Inspections Schedule regular inspections of the pump system. Check for any abnormalities, including unusual noises, leaks, or fluctuations in performance. Ensure that electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion.
2. Cleaning Procedures Pump components, especially the impeller and the casing, should be checked and cleaned periodically. Remove heavy solids and debris that may obstruct the pump’s operation. Depending on the operational environment, weekly or monthly cleaning might be necessary.
3. Lubrication Bearing and mechanical seal lubrication should be checked regularly, as adequate lubrication is crucial to preventing wear and reducing friction. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding lubrication intervals and types.
4. Testing of Motor and Controls Ensure that control panels and motor functions properly. Regular testing can help identify potential failures before issues arise, reducing downtime.
5. Seasonal Checks Seasonal maintenance is particularly critical in areas with harsh winters. Make sure that pumps are ready for changing weather conditions by ensuring they are clear of ice and debris.
Conclusion
Manual operation and diligent maintenance of submersible sewage pumping systems are critical for their efficiency and reliability in wastewater management. By adhering to safety protocols, conducting regular inspections, and performing timely maintenance tasks, operators can ensure these systems function optimally and serve their intended purpose without interruption. Understanding the nuances of manual operation not only empowers operators but also enhances the longevity of these essential components of sewage infrastructure.
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps Co., LTD.|Advanced Hydraulic Design&Energy-Efficient Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps Co., LTD.
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps Co., LTD.|energy-efficient fluid handling&industrial durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | Advanced Engineering&Industrial Efficiency
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | High Efficiency, Energy Saving
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump-Chi Yuan Pumps|High Efficiency&Reliable Performance
NewsJul.29,2025










