English
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Telephone: +86 13120555503
Email: frank@cypump.com
Nov . 09, 2024 11:18 Back to list
Optimizing Pump Service Efficiency for Enhanced Performance and Reliability
Understanding Pump Service Importance and Best Practices
In various industries, pumps play a crucial role in facilitating the movement and management of fluids. Whether it’s in water treatment plants, manufacturing facilities, or agricultural settings, the integrity and efficiency of pump systems are pivotal. Hence, understanding pump service becomes essential for ensuring reliability, efficiency, and longevity of the pumps in operation.
What is Pump Service?
Pump service refers to the range of activities required to maintain, troubleshoot, and repair pumps to ensure they operate at optimal performance levels. This encompasses preventive maintenance, routine inspections, and corrective actions when issues arise. Given that pumps are often subject to wear and tear due to continuous operation under demanding conditions, regular servicing is vital.
Importance of Regular Pump Service
1. Preventive Maintenance Regular service helps to identify potential problems before they become critical. Through routine inspections, wear indicators can be monitored, parts can be lubricated, and adjustments can be made. This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of unexpected failures.
2. Efficiency Improvement Over time, efficiency can deteriorate due to various factors such as corrosion, clogging, and component wear. A well-maintained pump operates at its best efficiency point, thus saving energy and reducing operational costs. Regular servicing can help restore or enhance this efficiency.
3. Longevity of Equipment Just as with any other mechanical system, timely service extends the life of pumps. Investing in regular maintenance can mitigate the frequency of repairs and the need for premature replacements, leading to long-term savings.
4. Safety Assurance Pumps that are not serviced regularly may pose safety hazards. Leaks, unintended discharge, or unexpected failures can lead to harmful accidents. Regular servicing ensures compliance with safety standards and helps in mitigating risks associated with pump operation.
Key Components of Pump Service
pump service
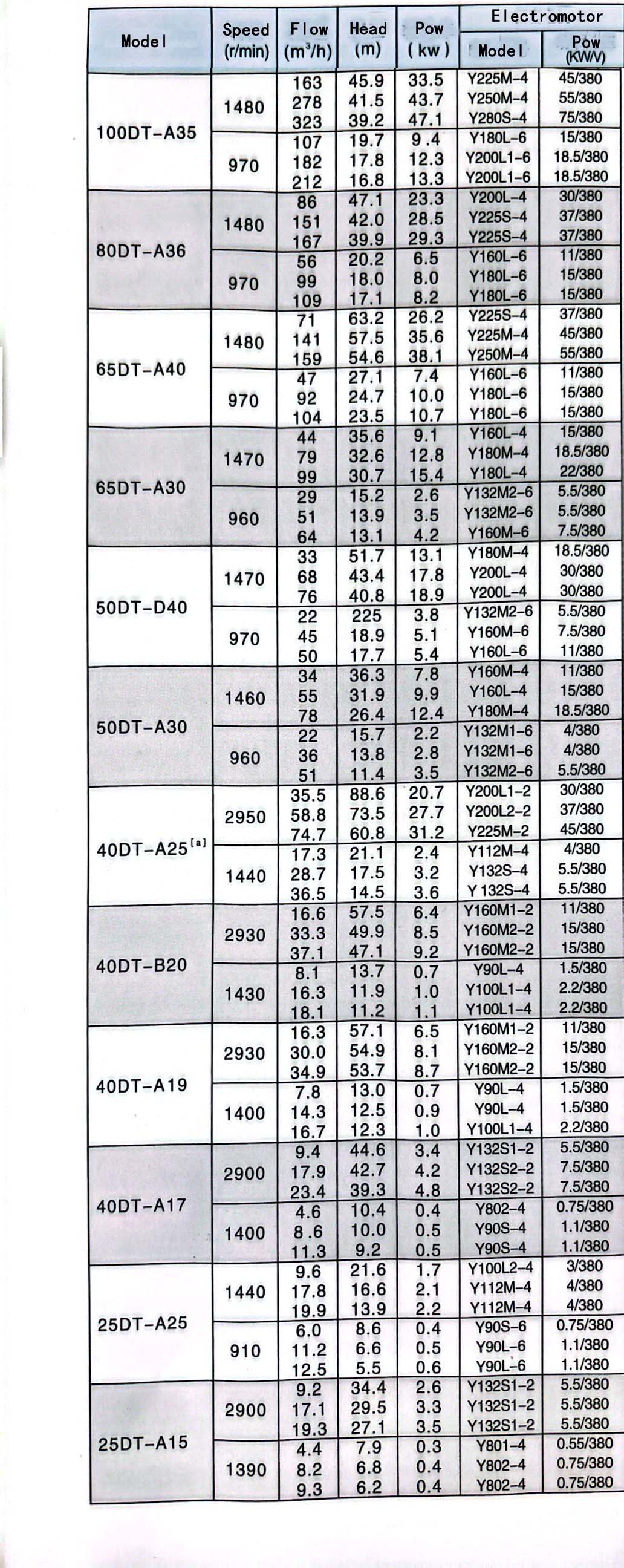
Implementing a comprehensive pump service strategy involves several key components
1. Inspection Regular inspections should include checking seals, bearings, and other critical components for signs of wear or damage. This should also involve monitoring fluid levels and examining connections for leaks.
2. Cleaning Pumps can become clogged with debris, sediment, or biofilm, particularly in applications involving water. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent efficiency losses and ensure that fluids can flow freely.
3. Lubrication Most pumps have moving parts that require lubrication to reduce friction. Establishing a lubrication schedule based on manufacturer guidelines is crucial.
4. Calibration and Adjustments Pumps should be calibrated to ensure they are operating within their designed parameters. Any adjustments needed to the system should be made promptly to maintain optimal performance.
5. Documentation Keeping accurate records of all maintenance activities is critical. This includes noting inspection results, repairs made, and parts replaced. Documentation aids in tracking performance over time and helps in future troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Investing in pump service is an investment in efficiency, safety, and operational reliability. By prioritizing preventive maintenance and adopting best practices, organizations can ensure that their pump systems function effectively, thereby avoiding costly downtime and repairs. As industries continue to evolve, understanding the dynamics of pump service will remain paramount in driving productivity and sustainability.
Whether you manage a small agricultural operation or a large manufacturing facility, recognizing the importance of pump service is crucial. By committing to regular maintenance and employing skilled professionals for service tasks, organizations can achieve peace of mind knowing that their fluid management systems are in top-notch condition, ready to meet any operational demands.
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps Co., LTD.
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps Co., LTD.|energy-efficient fluid handling&industrial durability
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | Advanced Engineering&Industrial Efficiency
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | High Efficiency, Energy Saving
NewsJul.30,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump-Chi Yuan Pumps|High Efficiency&Reliable Performance
NewsJul.29,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump|High Efficiency&Low Noise
NewsJul.29,2025










