Scottish Gaelic
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- igbo
- Indonesian
- irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- kazakh
- Khmer
- Rwandese
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Kyrgyz
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malgashi
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Mongolian
- Myanmar
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian
- Occitan
- Pashto
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Romanian
- Russian
- Samoan
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sesotho
- Shona
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uighur
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Welsh
- Bantu
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
Telephone: +86 13120555503
Email: frank@cypump.com
Sult . 14, 2024 11:56 Back to list
slurry pump power calculation
Power Calculation for Slurry Pumps An Overview
Slurry pumps are essential in various industrial applications, notably in mining, wastewater treatment, and dredging. These pumps are designed to handle mixtures of solids and liquids, commonly referred to as slurries. Understanding the power requirements for slurry pumps is crucial for efficient system design and operation. This article provides an overview of the factors influencing the power calculation for slurry pumps and the formula used to determine the necessary power.
The primary factors affecting the power calculation for a slurry pump include the specific gravity of the slurry, the flow rate, the total dynamic head (TDH), and the efficiency of the pump. The specific gravity indicates the density of the slurry relative to water and plays a significant role in determining the weight of the slurry being pumped. Higher specific gravity values usually indicate a more viscous and heavier slurry, which requires more power to move.
Power Calculation for Slurry Pumps An Overview
To calculate the power required for a slurry pump, engineers typically use the following formula
slurry pump power calculation
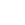
\[ P = \frac{(Q \times SG \times H)}{367 \times \eta} \]
Where - \( P \) = Power in kilowatts (kW) - \( Q \) = Flow rate in cubic meters per second (m³/s) - \( SG \) = Specific gravity of the slurry - \( H \) = Total dynamic head in meters (m) - \( \eta \) = Pump efficiency (a decimal representing the percentage, e.g., 0.85 for 85%)
This formula shows that as the flow rate, specific gravity, or total dynamic head increases, the required power for the pump also increases. Furthermore, understanding the pump’s efficiency is critical since a less efficient pump will require more power to achieve the same results.
In conclusion, accurately calculating the power requirements for a slurry pump is essential for optimizing performance and ensuring energy efficiency. By considering the specific gravity, flow rate, total dynamic head, and pump efficiency, operators can select the appropriate pump and motor size, significantly impacting operational effectiveness and cost efficiency in industrial applications.
-
Horizontal Split Case Pump with GPT-4 Turbo | High Efficiency
NewsAug.01,2025
-
ISG Series Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | High Efficiency, Durable Design
NewsAug.01,2025
-
Advanced Flue Gas Desulfurization Pump with GPT-4 Turbo | Durable & Efficient
NewsJul.31,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | Advanced Hydraulic Design&Durable Construction
NewsJul.31,2025
-
ISG Series Vertical Pipeline Pump - Chi Yuan Pumps | Energy Efficient & Low Noise
NewsJul.31,2025
-
pipeline pump - Chi Yuan Pumps Co., LTD.|High Efficiency&Low Noise
NewsJul.31,2025










